Musicianship Resources
Syncopation in pop/rock music
Syncopation occurs when a rhythmic pattern that typically occurs on strong beats or strong parts of the beat occurs instead on weak beats or weak parts of the beat. Most pop/rock songs have a mixture of syncopated and "straight" rhythms. The syncopated rhythms are usually easy to sing, since they often match speech better than straight rhythms, but they are more difficult than straight rhythms to sight-sing, dictate, or transcribe.
Beats and syncopations
In contemporary pop/rock music, syncopation typically involves taking a series of notes of equal durations, cutting the duration of the first note in half, and shifting the rest early by that half duration.
For example, a series of four quarter notes, all sounding on the beat, can be transformed in this way by making the first note into an eighth note, and sounding each successive quarter note on eighth note early—all on the offbeats.
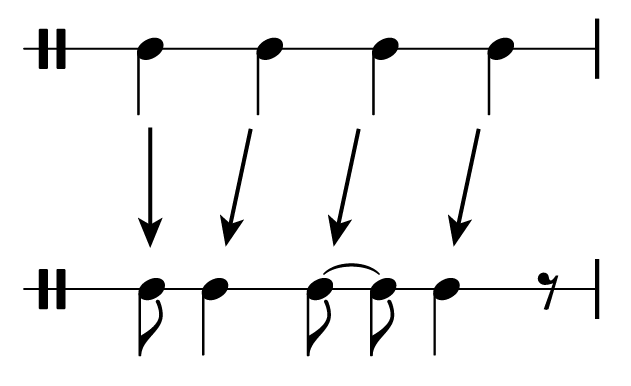
(Note the use of a tie to make beat three clear. Always do this when notating simple quadruple meter in order to make it easy to read.)
This process can occur on any metrical level. If the duration of the series of "straight" notes is two beats, they will be syncopated by changing the first note to a single beat and shifting each other note early by a beat. If the duration of the straight notes, like the figure above, is a beat, they will be syncopated by a division (one half beat in simple meter). If the straight notes are each divisions, they will be syncopated by shifting each note by a subdivision. The unit of syncopation (the duration of the first note, and the amount of shift applied to the following notes) is always half of the duration of the straight notes. All of these syncopations are realtively common in contemporary pop/rock music.
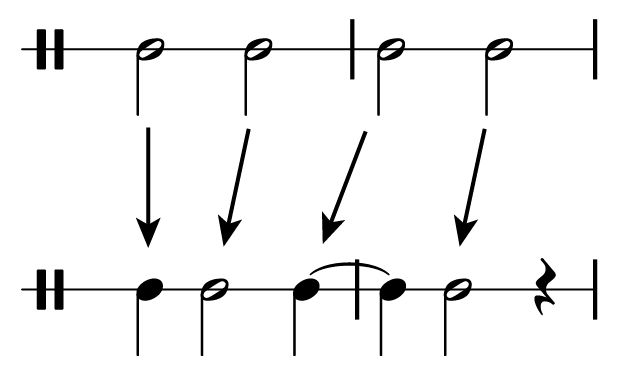
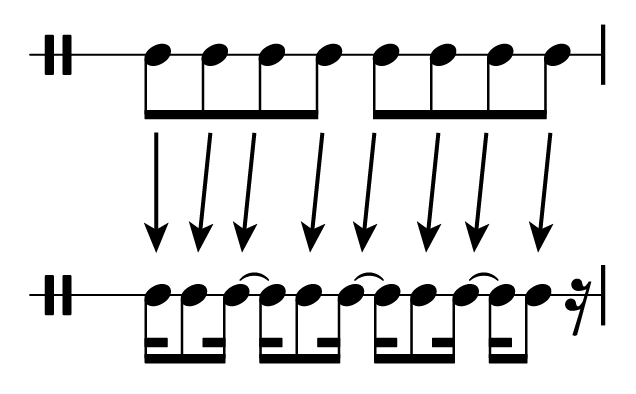
(Note the use of ties to make each beat clear. Always do this in order to make it easy to read.)
Transcribing syncopated rhythms
Syncopated rhythms are easily identified by the frequently occuring off-beat rhythms. For example, if you conduct or tap the counting pulse while listening to a song, several notes in a row that are articulated between your taps or conducted beats, with no notes articulated simultaneously with the counting pulse, indicate syncopation.
Once you identify a syncopated passage—which may only involve two or three notes—figure out on what metrical level the syncopation occurs. For example, in simple meter, if no notes are articulated directly on the counting pulse beats and one note is articulated in between each beat, the syncopation is occuring at the beat level. If no notes are articulated directly on the counting pulse beats and two notes are articulated in between each beat, listen to the passage again while tapping the division. If no notes are articulated directly on the division taps and one note is articulated in between each tap, the syncopation is occuring at the division level.
Once you have determined the metrical level on which the syncopation occurs, determine the durational value of the shift. If the syncopation occurs on the beat level (one note sounding between each counting pulse beat), the value of syncopation is a division: each beat-length note has been shifted one division early. If the syncopation occurs on the division level, the value of syncopation is a subdivision: each division-length note has been shifted one subdivision early.
Lastly, determine how the syncopated pattern begins. Does the offbeat pattern simply begin offbeat? Or does the pattern begin with two quick notes back-to-back as above—one short note on the beat followed by the first of the longer syncopated notes?
Once you have determinted the level of syncopation, the duration of the shift, and whether or not the pattern begins with a truncated onbeat note, the rhythmic pattern should be easy to notate. If, however, you are still having difficulty, try using the lyric syllables and the stress patterns of the poetry to help you keep track of the individual notes and which ones are on/offbeat.
Demo
In the following video, I walk through this process in the song "Shh" by Frou Frou.